Introduction
Retrieval (图搜) 也是CV领域一个应用非常广泛的方向,在安防场景下,我们常常会根据摄像头抓怕的嫌疑人头像去人脸数据库里进行搜索;在电商平台,用户也会拍摄图片进行上传,我们的算法应返回对应的SKU,此为“拍照购”。Retrieval的难点主要在于如何训练表示能力良好的embedding模型,以及如何高效地进行feature similarity searching,尤其是库里SKU种类达到亿级别的时候,为了保证良好的用户体验,如何能快速而准确地给用户返回匹配信息,是一直以来不少研究者和工程师致力于解决的问题。由于Deep Learning的飞速发展,Retrieval在工业应用方面越来越成熟,常规流程如下:
- 训练embedding模型,可视为一个Classification或Metric Learning问题
- 如果对检索速度有高要求,可能需要做Hash或Quantization
- 利用FAISS做大规模相似性搜索
- Similarity衡量标准一般是$L_2$ distance或Cosine Similarity
本文主要分享一些读过的顶会/顶刊上的paper。
@LucasXU注:本文长期更新。
Supervised Deep Hashing for Scalable Face Image Retrieval
Paper: Supervised Deep Hashing for Scalable Face Image Retrieval
这是一篇Face Retrieval方向的文章,整体framework和idea也非常简单:
- Deep hash的引入,Multi-task Loss: 同时优化Classification Loss和Quantization Loss。
- low-level和high-level information的fusion,来获取multi-scale的信息
因Retrieval场景的特殊性(亿级别的item + 高维特征向量匹配),以及用户对速度与精度的需求,不少Retrieval方法会采用Hashing来生成图像的compact binary codes,而binary codes的Similarity Search会非常快:
- Hamming distance的计算可以仅通过XOR operation得到。
- 将highly compressed data加载进内存,减小了大容量内存的需求。
当前的hashing方法主要有两种:
- Data-independent: 使用random projection来产生binary codes,例如Locality-Sensitive Hashing (LSH)。
- Data-dependent: 在尽可能保留data structure的情况下从数据中学习Hashing function。
而Learning-based Hashing methods又可以被分为unsupervised hashing (例如random projection, reconstruction error minimization, graph-based hashing, quantization error minimization) 和supervised hashing两类。
本文模型网络结构图如下: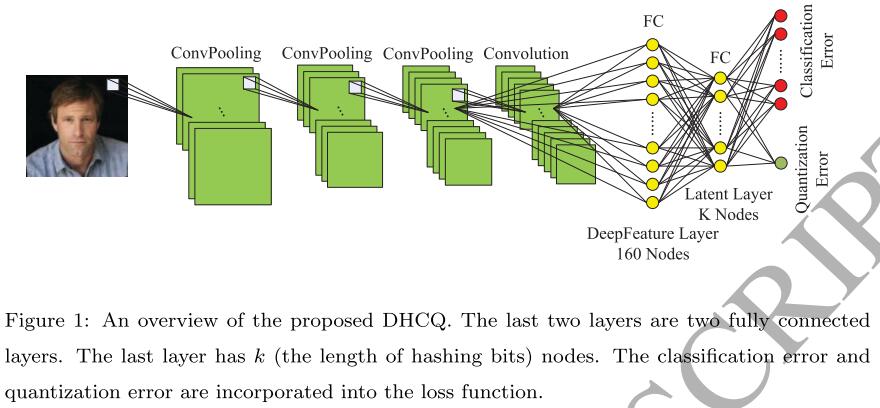
Learning-based hashing methods旨在学习某种hashing function来为每张图生成compact binary codes,即$X\to B\in \{0,1\}^{k\times N}$,$k$为binary codes的length。
在实验中,作者用了一种非常Naive的方法来进行quantize,即将最后一个隐层的输出作为sigmoid function的输入,使其被squeeze到$(0, 1)$区间,然后再通过符号函数二值化:
$$
sign(x)=\begin{cases}
1 & if x\geq 0.5 \\
0 & otherwise
\end{cases}
$$
Softmax Loss作为classification loss,$L_2$ loss作为quantization loss:
$$
min |B-H|_F^2
$$
其中,$B=sign(H)$,通过优化quantization loss,$H$会越来越接近1或者0。
实验中,作者发现,classification criterion比quantization loss在explore discriminative information方面更重要。
Reference
- Zhao, Bo, et al. “Memory-augmented attribute manipulation networks for interactive fashion search.” Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2017.
- Chum, Ondrej, et al. “Total recall: Automatic query expansion with a generative feature model for object retrieval.” 2007 IEEE 11th International Conference on Computer Vision. IEEE, 2007.
- Tang, Jinhui, Zechao Li, and Xiang Zhu. “Supervised deep hashing for scalable face image retrieval.” Pattern Recognition 75 (2018): 25-32.
- Radenović, Filip, Giorgos Tolias, and Ondrej Chum. “Fine-tuning CNN image retrieval with no human annotation.” IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence (2018).
- Babenko, Artem, and Victor Lempitsky. “Aggregating local deep features for image retrieval.” Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision. 2015.
- Mousavian, Arsalan, and Jana Kosecka. “Deep convolutional features for image based retrieval and scene categorization.” arXiv preprint arXiv:1509.06033 (2015).
- Gordo, Albert, et al. “Deep image retrieval: Learning global representations for image search.” European conference on computer vision. Springer, Cham, 2016.
- Huang, Junshi, et al. “Cross-domain image retrieval with a dual attribute-aware ranking network.” Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision. 2015.
- Xie, Lingxi, et al. “Image classification and retrieval are one.” Proceedings of the 5th ACM on International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval. Acm, 2015.
