Introduction
做Vision的同学们对Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN)一定不会陌生,可以毫不夸张的说,现如今绝大多数的视觉问题,都是由CNN驱动的。从LeNet到如今的ResNet、DenseNet、CliqueNet,CNN的结构发生了很大的变化。本文旨在记录CNN的基础构件。
Basic of CNN
Convolution
- VALID:无论怎样都不使用zero padding,并且filter只允许访问那些图像中能够完全包含整个核的位置。
- SAME:只进行足够的zero padding来保持输出和输入具有相同的大小;然而输入像素中靠近边缘的部分相比于中间部分对于输入像素的影响更小。这可能会导致边界像素存在一定程度的欠表示。
- FULL:它进行了足够多的zero padding,使得每个像素在每个方向上恰好被访问了$k$次,最终输出图像的宽度为$m+k-1$。这种情况下,输出像素中靠近边界的部分相比于中间部分是更少像素的函数。这将导致学得一个在卷积特征映射的所有位置都表现不错的单核更为困难。
Pooling
无论采用什么样的Pooling,当输入做少量变动时,Pooling能够 帮助输入的表示近似不变。Shift Invariant指得是当我们对输入进行少量平移时,经过Pooling后的大多数输出并不会发生改变。例如MaxPooling中,Pooling只对周围的最大值比较敏感,而不是对精确的位置。
- Average Pooling通过对邻域内特征数值求平均来实现,能够抑制由于邻域大小受限造成估计值方差增大的现象,
特点是对背景的保留效果更好。 - Max Pooling通过取邻域内特征最大值来实现,能够抑制网络参数误差造成估计均值偏移的现象,特点是
更好地提取纹理信息。 - Min Pooling通过取邻域内特征最小值来实现,能够提取所有类别中的通用特制,而非偏好某个category。Min Pooling在Image Quality Analysis以及Coarse and Fine Classification任务中经常被用到(例如[4]和[5])。
Variants of Convolution
除了传统的卷积,其实还有很多种卷积方式(例如DW Conv/Dilation Conv),在这里就对笔者认为比较insightful的Conv Filter进行一下讲解。
Dilation Convolution
Dilation conv允许我们在不损失resolution的情况下将multi-scale的information做融合,而multi-scale information对于Classification/Detection/Segmentation都是非常重要的。
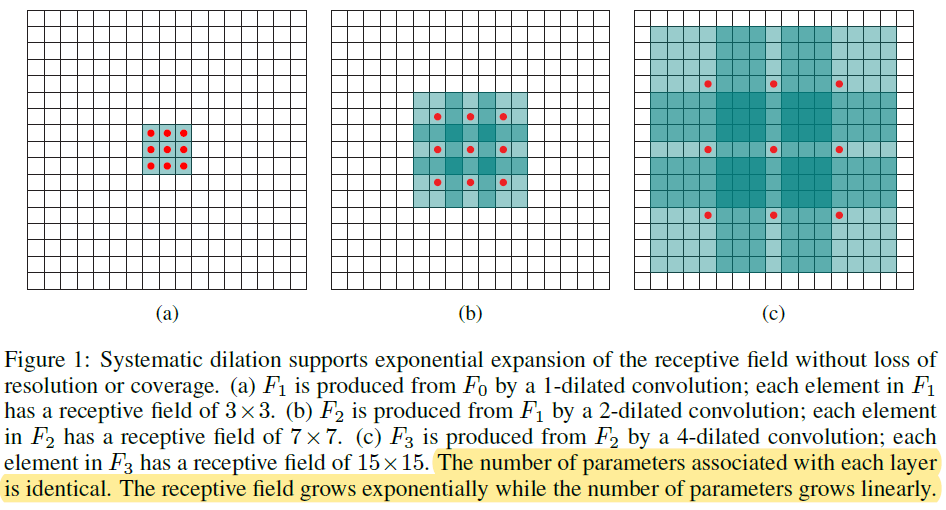
Unlike pyramid-shaped architectures carried over from image classification, the presented context module is designed specifically for dense prediction. It is a rectangular prism of convolutional layers, with no pooling or subsampling. The module is based on dilated convolutions, which support exponential expansion of the receptive field without loss of resolution or coverage.
Define the receptive field of an element $p$ in $F_{i+1}$ as the set of elements in F0 that modify the value of $F_{i+1}(p)$. Let the size of the receptive field of $p$ in $F_{i+1}$ be the number of these elements. It is easy to see that the size of the receptive field of each element in $F_{i+1}$ is $(2^{i+2}-1)\times (2^{i+2}-1)$. The receptive field is a square of exponentially increasing size.
Neural Network. Wide & Shallow VS Deep & Thin?
在DeepLearning Book这本书的Chapter 6.4中,作者通过实验发现,浅层模型在参数数量达到2000万时就过拟合,而深层模型在参数数量超过6000万时仍然表现良好。这表明,使用深层模型表达出了对模型可以学习的函数空间的有用偏好。具体来说,它表达了这样一种认知,即该函数应该由许多更简单的函数复合在一起而得到。这可能导致学习由更简单的表示所组成的表示(例如,由边所定义的角)或者学习具有顺序依赖步骤的程序(例如,首先定位一组对象,然后分割它们,之后识别它们)。
但是,有研究者设计了Wide Residual Networks这种结构,与vanilla ResNet相比,WRN就属于wide & deep,但是却取得了比counterpart ResNet更好的精度、更快的训练时间。所以到底是要deep还是要wide,也不能一概而论(参考Machine Leaning中的No-free-launch)。
Reference
- Goodfellow, Ian, et al. Deep learning. Vol. 1. Cambridge: MIT press, 2016.
- Yu, Fisher, and Vladlen Koltun. “Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions.”//ICLR 2016.
- Zagoruyko S, Komodakis N. Wide residual networks[J]. BMVC, 2017.
- Lei J, Guo Z, Wang Y. Weakly supervised image classification with coarse and fine labels[C]//2017 14th Conference on Computer and Robot Vision (CRV). IEEE, 2017: 240-247.
- Goo W, Kim J, Kim G, et al. Taxonomy-regularized semantic deep convolutional neural networks[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, Cham, 2016: 86-101.
