Introduction
Image Quality Assessment (IQA) 是计算机视觉领域一个非常重要的研究方向,并且在许多方向也有着非常好的落地场景(例如在滴滴出行,就需要设计算法来实现对网约车司机上传的证件照进行图像质量分析,若存在大规模的反光(reflection)、模糊(blur)等,就需要予以拒绝);此外,IQA也常常被用于Face Anti-Spoofing,因为有时候print/replay attack的图片/视频 和活体相比,其图像质量往往会比较差(例如颜色失真、反光、模糊、变形等),因此也是一个非常显著的特征。
IQA主要分为3种:(1) 将distorted image和original image进行质量比较的,称为full reference。(2) 当reference image不可获取时,称为no-reference。(3) 当reference image只有部分可以获取时,称为reduced reference。
IQA主要的Metric是MSE, PSNR (Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio)、SROCC(Spearman Rank Order Correlation Coefficien)、LCC(Linear Correlation Coefficien) 和 SSMI (structural similarity)。
MSE measures pixel-wise error of two images
SROCC measures how well one quantity can be described as a monotonic function of another quantity.
$$
SROCC=\frac{1-6\sum_{i=1}^n d_i^2}{(n-1)n(n+1)}
$$PLCC measures the linear dependence between two quantities, -1 is the standard measure for regression where +1 denotes perfect positive correlation and −1 perfect negative correlation. Values near zero de- note poor correlation. In image quality assessment PLCC is used to measure the linear correlation between the true subjective and method predicted scores.
$$
PLCC=\frac{\sum_{i=1}^n (s_i-\bar{s})(q_i-\bar{q})}{\sqrt{\sum_{i=1}^n (s_i-\bar{s})^2} \sqrt{\sum_{i=1}^n (q_i-\bar{q})^2}}
$$
where $d_i$ is the rank-order difference between the i-th image indeces in the sorted lists of the subjective ground truth and predicted scores.
@LucasXU注:本文长期更新。
Convolutional neural networks for no-reference image quality assessment
Paper: Convolutional neural networks for no-reference image quality assessment
这是CVPR’14的paper,应该是最早将CNN用在NR-IQA领域的paper,idea非常简单(貌似早些年的paper都是如此),作者设计了一个simple CNN来回归quality score,但与常规CNN结构不同的是,作者同时使用了MinPool与MaxPool,然后将pooled feature做拼接,在送入后续的FC layers(关于MinPooling的作用作者没说,只是能涨点)。
熟悉DL的同学都知道,AlexNet最早在NIPS’2012就已经出现了,那为啥在这段时间没人将其应用在NR-IQA呢?作者这里也给出了了原因:
Object recognition中的CNN设计主要是为了encode local invariant part feature,而IQA则是为了capture image quality。在NR-IQA任务中,良好的特征应该能够capture NSS(Natural Scene Statistics) property。
那么什么是NSS property?这里引用CVPR原文上的一段话吧,也很好理解:
Typically, NSS based features characterize the distributions of certain filter responses. Traditional NSS based features are extracted in image transformation domains using, for example the wavelet transform or the DCT transform. These methods are usually very slow due to the use of computationally expensive image transformations.
CNN for NR-IQA
本文的网络结构如下: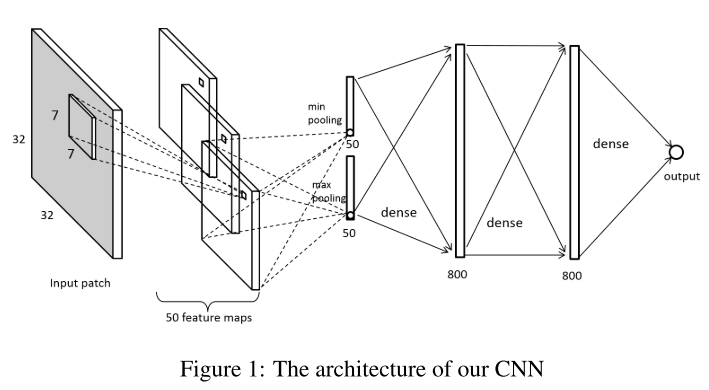
注:
作者先将输入图片转成灰度,然后做contrast normalization(注:contrast norm应用在patch上,而非entire image)、sample不重叠的 $32\times 32$ patch去训练IQANet,最终每张图中$N$个patch的quality score均值即为该图的quality score,loss function为MSE。
Multi-task CNN for IQA
Paper: Simultaneous estimation of image quality and distortion via multi-task convolutional neural networks
这篇是上述团队发表于ICIP’2015的工作,是对那篇CVPR’14的改进版本,提出了一个multi-task CNN结构,即同时regress quality score与预测distortion type,总体上也非常简单,详情可以去阅读原paper,这里记录一下几个关键点吧。
注:
和IQANet一样,回归quality score是一张图中多个patch的平均值,而图像的distortion则通过patch的majority voting得来。
IQACNN++网络结构如下:比IQANet深了一些(但其实依然不算太deep),依然同时使用了MinPool和MaxPool: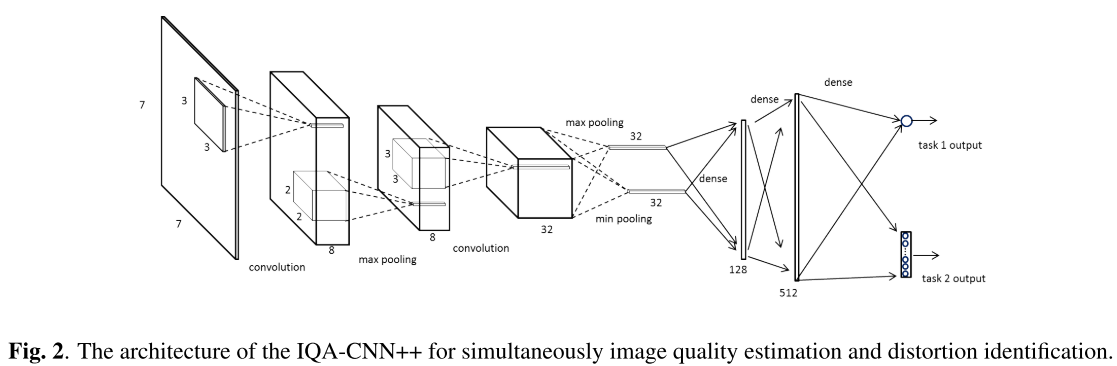
NIMA
NIMA是Google发表在TIP’18上的工作,其实整体idea也是非常简单:用图像分类的SOTA网络(例如VGG、GoogLeNet、MobileNet)来评估图像美学质量。传统的Image Aesthetic Estimation方法大多直接分类(low quality/high quality),或直接回归(mean quality score regression)。但本文旨在使模型预测值与真实值有更高的correlation,因此作者使用了EMD (earth mover's distance) loss,该loss被证明在对ordered class classification任务上有明显提升。
Delve into NIMA
人类对图像打分的分布可以表示为一种empirical probability mass function $p=[p_{s_1}, \cdots, p_{s_N}]$,其中$p_{s_1}\leq p_{s_i}\leq p_{s_N}$,其中$p_{s_i}$代表第$i$个score bucket,$N$代表bucket总数。因$\sum_{i=1}^N p_{s_i}=1$,$p_{s_i}$代表quality score落入第$i$个bucket的概率。令打分的分布为$p$,平均分为$\mu=\sum_{i=1}^N s_i\times p_{s_i}$,标准差为$\delta=(\sum_{i=1}^N (s_i-\mu)^2)^{\frac{1}{2}}$。优化目标即为找到最优probability mass function $\hat{p}$(即对$p$最准确的估计)。
Loss Function
Softmax Cross-Entropy被广泛应用于多分类任务,其数学表达如下:
$$
\sum_{i=1}^N -p_{s_i}log(\hat{p}_{s_i})
$$
其中$\hat{p}_{s_i}$代表最大化正确预测类别概率的第$i$个score bucket。由上述公式可知,cross-entropy是orderless的。但是图像美学评估实际上是个ordered-class任务,而cross-entropy缺乏不同score bucket之间的inter-class relationship。那么如何处理这种场景呢?一种常见的做法是带入regression framework,本文采取了另外一种做法:
对于image quality ratings,类别可排序为$s_1\leq \cdots \leq s_N$,不同类别的r-norm距离可表示为$||s_i-s_j||_r$,EMD定义为移动一种分布到另一种分布的最小代价。Groundtruth probability mass function为$p$,estimated probability mass function为$\hat{p}$,则Normalized Earth Mover’s Distance可以表示为:
$$
EMD(p, \hat{p})=(\frac{1}{N}\sum_{k=1}^N |CDF_p(k)-CDF_{\hat{p}}(k)|^r)^{\frac{1}{r}}
$$
其中$CDF_p(k)$为cumulative distribution function $\sum_{i=1}^kp_{s_i}$。上式close-form solution需要distribution有相同的mass,即$\sum_{i=1}^kp_{s_i}=\sum_{i=1}^k\hat{p}_{s_i}=1$。
实验结果也是各种好,一句话总结吧:
Our models effectively predict the distribution of quality ratings, rather than just the mean scores. This leads to a more accurate quality prediction with higher correlation to the ground truth ratings.
BLINDER
Paper: Blind image quality prediction by exploiting multi-level deep representations
这也是一篇非常简单的paper,核心idea如下:
- 利用ImageNet pretrained VGG提取multi-level feature
- 对每个不同level的feature map做MinPool和MaxPool,然后再concatenate
- 回归多个SVR,average score ensemble
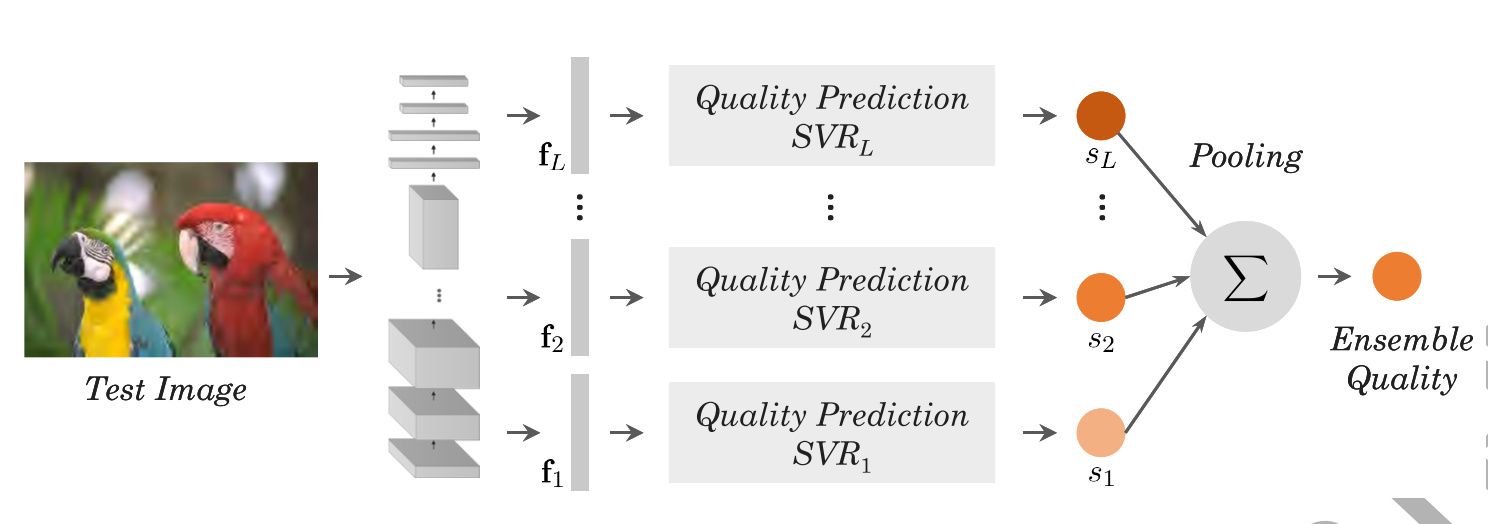
方法虽然简单,但是效果貌似还很不错。作者在实验部分还发现了以下现象:
- relu/mpool层的效果比它前面的conv/fc层的效果差,原因可能是relu的非负性丢失了部分信息(所以这就是IQA领域喜欢结合MinPool和MaxPool一起用的原因?)
- 接近softmax层的效果correlation比较高,说明object recognition信息能够和image quality信息互补
Reference
- Z. Wang, A. C. Bovik, H. R. Sheikh and E. P. Simoncelli, “Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity,” IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, vol. 13, no. 4, pp. 600-612, Apr. 2004.
- Talebi, Hossein, and Peyman Milanfar. “Nima: Neural image assessment.” IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 27.8 (2018): 3998-4011.
- Kang, Le, et al. “Convolutional neural networks for no-reference image quality assessment.” Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2014.
- Kang, Le, et al. “Simultaneous estimation of image quality and distortion via multi-task convolutional neural networks.” 2015 IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP). IEEE, 2015.
- Gao F, Yu J, Zhu S, et al. Blind image quality prediction by exploiting multi-level deep representations[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2018, 81: 432-442.
- Bianco S, Celona L, Napoletano P, et al. On the use of deep learning for blind image quality assessment[J]. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2018, 12(2): 355-362.
