Introduction
Siamese Network也是一个比较有意思的网络结构,并且在许多领域都有了非常成功的应用,本文主要记录这些具体的application中一些代表性的paper。
@LucasXU注:对网络结构感兴趣的可以阅读我的另外一篇文章Architecture。
Siamese Network
Paper: Signature verification using a “siamese” time delay neural network
这算是Siamese Network最早的一篇文章了,记录了用Siamese Network做signature verification的应用。整体上比较简单,就记录一下key points吧。
- 本文中用到的Siamese Network是两个identical subnetwork,来从两张input image中提取feature,那么verification就是比较extracted feature和该signer之前保存的signature的feature vector之间的distance。
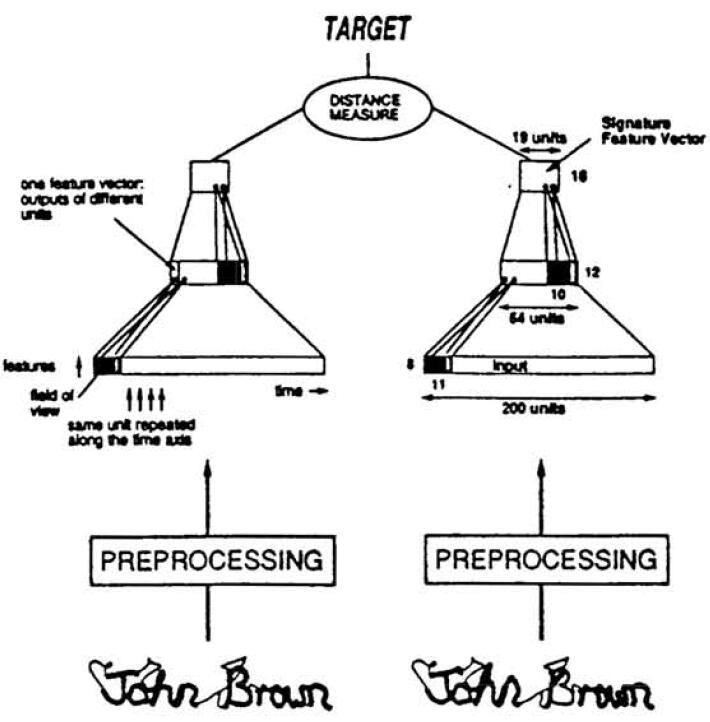
- 网络中所有的weights都是learnable,但是两个subnetwork被限制于weights都是相同的。
- 在Testing的时候,只用到其中一个subnetwork的输出作为feature vector,来和stored signature feature vector进行比对distance。
Siamese neural networks for One-shot Image Recognition
Paper: Siamese neural networks for one-shot image recognition
这是一篇发表在ICML’15上的Paper,主要讲的是用Siamese Network做one-shot learning,在讲解这篇paper之前,先来介绍几个概念吧。
- One-shot Learning: 在多分类问题中,对于每一个类,我们只观察一个sample。
- Zero-shot Learning: 任何一个sample都不能给模型观测。
Deep Siamese Networks for Image Verification
先上基础的Siamese Network的网络结构,大致是这样的: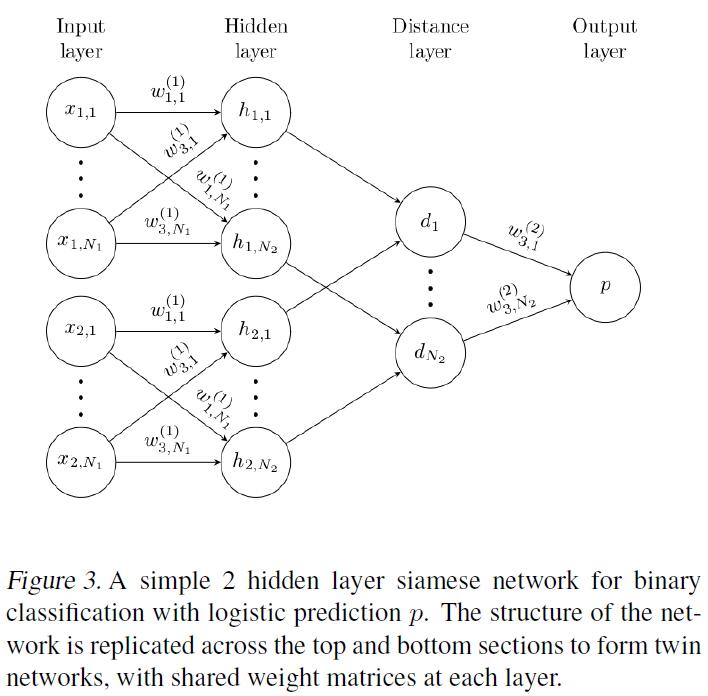
本文采用twin feature $h_1$与$h_2$之间加权的$L_1$ distance,并结合sigmoid map到$[0, 1]$区间,来作为metric。
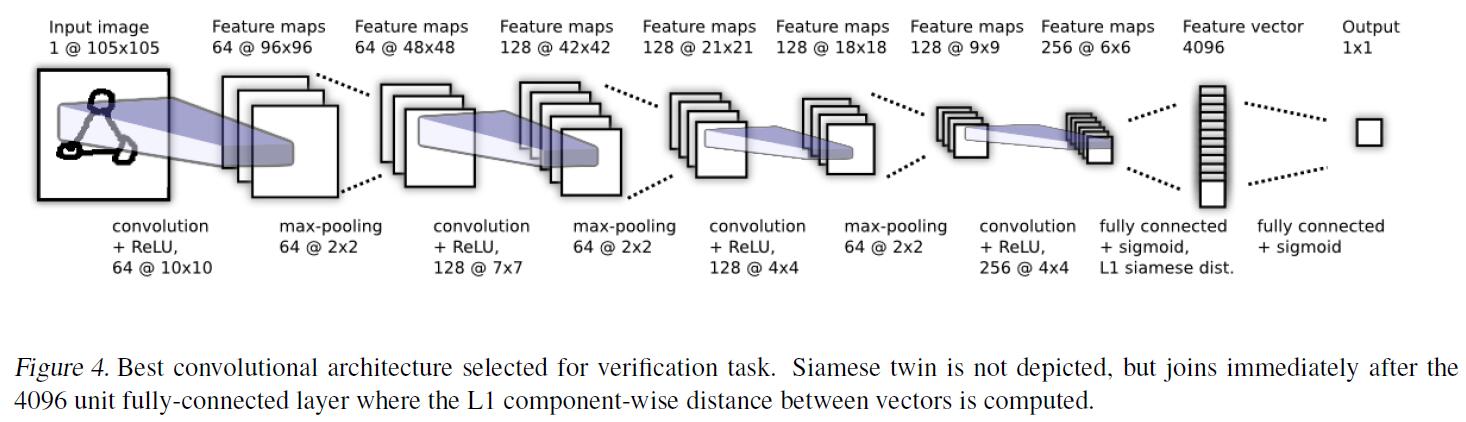
上述是本文用到的Convolutional Siamese Architecture,最后一个conv layer的feature map被flatten成feature vector,然后紧跟另一个layer用来计算每个siamese twin的induced distance,再作为sigmoid function的输入。即:
$$
p=\sigma(\sum_j \alpha_j |h_{1,L-1}^{(j)} - h_{2,L-1}^{(j)}|)
$$
$\alpha_j$是衡量component-wise distance的权重,通过training过程中自动学习。网络的最后一层向$(L-1)$-th hidden layer的learned feature space引入了一种metric来衡量feature vector的similarity。
Loss Function
设$M$为mini-batch size,$i$代表第$i$个batch。令$y(x_1^{(i)}, x_2^{(i)})$为M-dimensional feature vector。若$x_1$和$x_2$为相同class,则$y(x_1^{(i)}, x_2^{(i)})=1$;反之$y(x_1^{(i)}, x_2^{(i)})=0$。采用Cross Entropy作为loss:
$$
\mathcal{L}(x_1^{(i)}, x_2^{(i)})=y(x_1^{(i)}, x_2^{(i)})log p(x_1^{(i)}, x_2^{(i)}) + (1- y(x_1^{(i)}, x_2^{(i)}))log (1-p(x_1^{(i)}, x_2^{(i)})) + \lambda^T |w|^2
$$
One-shot Learning
当网络训练完成,就可以用one-shot learning来测试learned feature的generalization ability。
Suppose we are given a test image $x$, some column vector which we wish to classify into one of $C$ categories. We are also given some other images $\{x_c\}_{c=1}^C$, a set of column vectors representing examples of each of those $C$ categories. We can now query the network using $x$, $x_c$ as our input for a range of $c=1,\cdots,C^2$. Then predict the class corresponding to the maximum similarity.
$$
C^{\star}=\mathop{argmax} \limits_{c} p^{(c)}
$$
Siamese Network in Visual Tracking
Paper: Learning by tracking: Siamese cnn for robust target association
这是一篇利用Siamese Network做tracking的paper,由于关注点并非visual tracking,所以这里只记录Siamese Network的设计和使用部分。
本文用到的tracking framework主要idea如下:
- 利用CNN学习local-spatio-temporal features
- 学习contextual features来encode position variants
- XGBoost来对combined features(local + contextual)进行classification
涉及到matching问题,一个很自然的idea就是使用Siamese Network + Contrastive Loss。Siamese Network的组合方式有如下3种:
- Cost Function: Input patches are processed by two parallel branches featuring the same network structure and weights. Finally, the top layers of each branch are fed to a cost function [12, 49] that aims at learning a manifold where different classes are easily separable.
- In-Network: The top layers of the parallel branches processing the two different inputs are concatenated and some more layers are added on top of that [21, 62]. Finally, the standard softmax log-loss function is employed.
- Joint data input: The two input patches are stacked together forming a unified input to the CNN [21]. Again, the softmax log-loss function is used here.
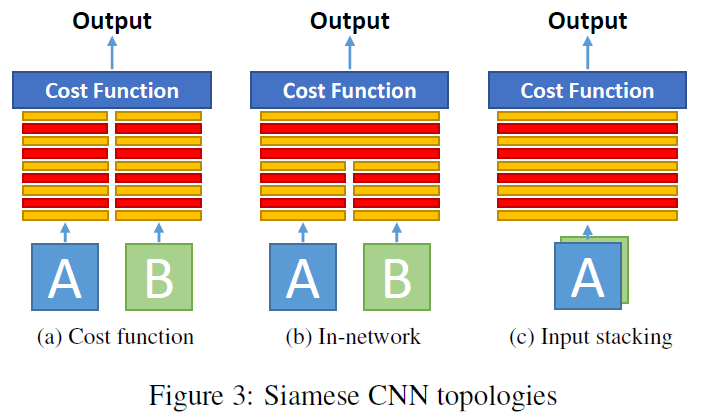
网络结构是这样的:![]()
Input接受4种类型的information,即待比对的patch(normalized LUV color space) $I_1$和$I_2$,对应的optical flow components $O_1$和$O_2$。
- Loss of Siamese Network:
$E=\frac{1}{2N}\sum_{n=1}^N (y)d + (1-y)max(\tau - d,0)$
其中,$d=|a_n-b_n|_2^2$代表$twin-subnetwork$顶层FC layer输出 $a_n$和$b_n$的$L_2$ normalized response。 - CNN的结构:先走conv layer with PreReLU $C_{1,2,3}$;然后是max-pooling layer来使得网络对miss alignment更加robust;然后是fully-connected layers $F_{4,5,6,7}$来capture图片中distant parts features的correlation、以及cross-modal的dependencies;最后一个FC layer的输出进入到binary softmax layer,来产生class label (match/no match)的distribution。$F_6$的输出被用作raw patch matching的feature vector。
- Data augmentation: geometric distortion (rotation, translation, skewing, scaling, flipping); image distortion (guassian blur, noise, gamma).
Reference
- Bromley, Jane, et al. “Signature verification using a” siamese” time delay neural network.” Advances in neural information processing systems. 1994.
- Koch, Gregory, Richard Zemel, and Ruslan Salakhutdinov. “Siamese neural networks for one-shot image recognition.” ICML Deep Learning Workshop. Vol. 2. 2015.
- Leal-Taixé, Laura, Cristian Canton-Ferrer, and Konrad Schindler. “Learning by tracking: Siamese cnn for robust target association.” Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. 2016.
- Siamese Networks: Algorithm, Applications And PyTorch Implementation
