Background
- PyTorch 模型训练时的预处理环节与实车部署环节无法完全对齐,我们回灌 case 发现:PyTorch 模型表现正常,但 fp32 & fp16 的 trt 模型存在线弯折、左右甩等异常现象。模型对上游的一些 perturbation 过于敏感,希望在训练过程中增强鲁棒性。
- 不同初始化&训练方式对模型的 robustness、generality 有较大的影响,需要在训练过程中选择最优的训练方式。
Methods
Are All Layers Created Equal?
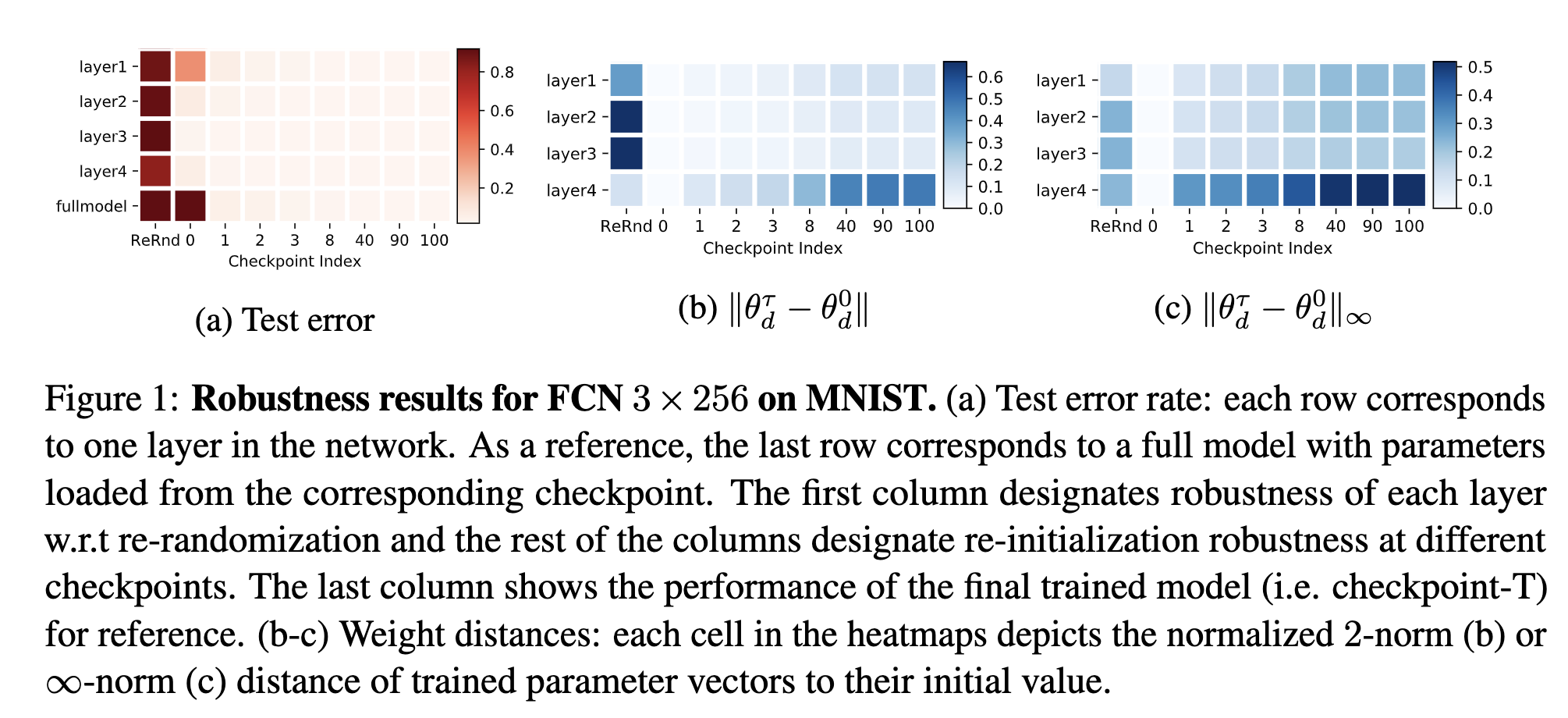
主要结论:
- DL 模型中,不同 layer 的重要性其实是不同的,low-level layers 在训练过程中更新得更激进,high-level layers 相对缓和一些
- re-initialization 效果优于 re-randomization,paper 里验证了 re-initialization 的方式能提升模型鲁棒性
Fast Gradient Sign Method
Adversarial training 能够 (1)提高模型应对恶意对抗样本时的鲁棒性;(2)作为一种 regularization,减少 overfitting,提高泛化能力。FGSM 算法 pipeline 如下:
- Calculate the loss after forward propagation,
- Calculate the gradient with respect to the pixels of the image,
- Nudge the pixels of the image ever so slightly in the direction of the calculated gradients that maximize the loss calculated above
Averaging Weights Leads to Wider Optima and Better Generalization
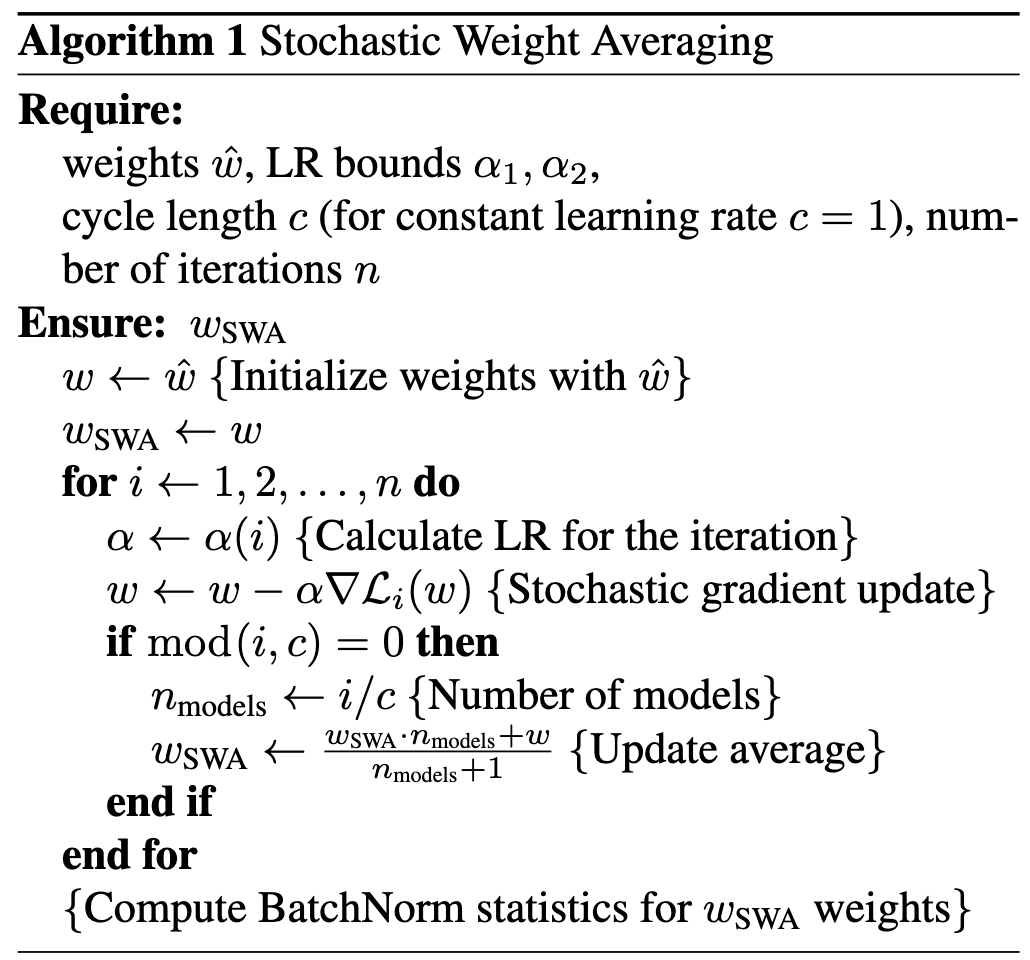
通过将训练过程中多个 snapshot 的 checkpoint 进行 weight averaging,得到 wider optima (& better generalization)。这个 idea 属于 semi-supervised learning 里常用的 tricks 了,确实很 work。方法非常简单,并且 PyTorch 也集成了 SWA 和 EMA 的实现:
此外,也有论文验证了简单将 SWA 应用在 object detection & segmentation 任务中,也能带来提升。
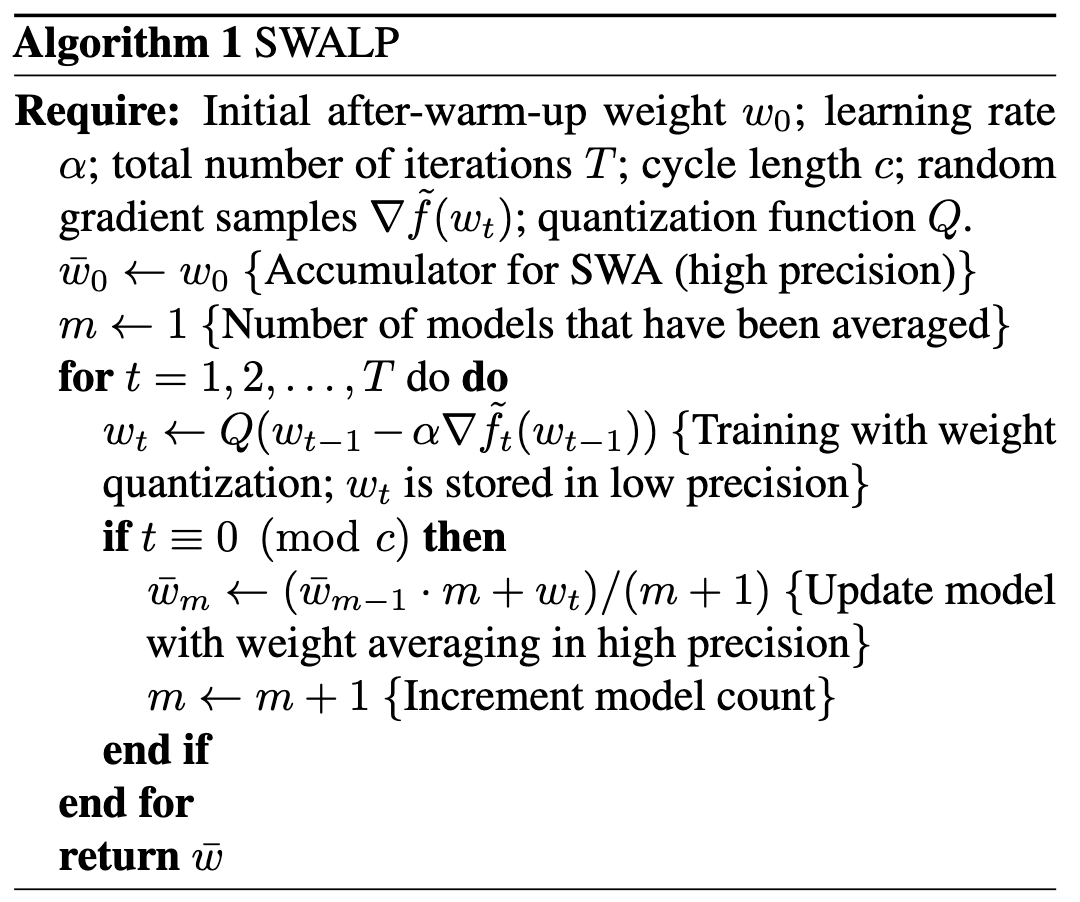
以及…在 quantized training 过程中引入 SWA 也能使得模型对 quantization noise 更加鲁棒。
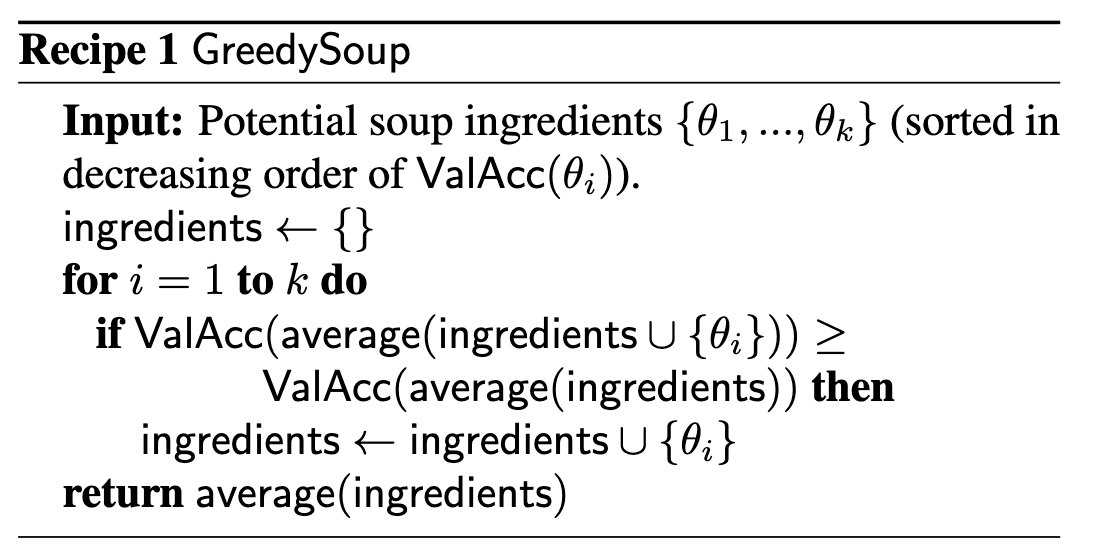
Model Soups
一共提出来 3 种 model soups 方案(uniform soup, greedy soup, learned soup),通过 averaging model weights 就能得到性能提升。其中最有效的是 greedy soup:
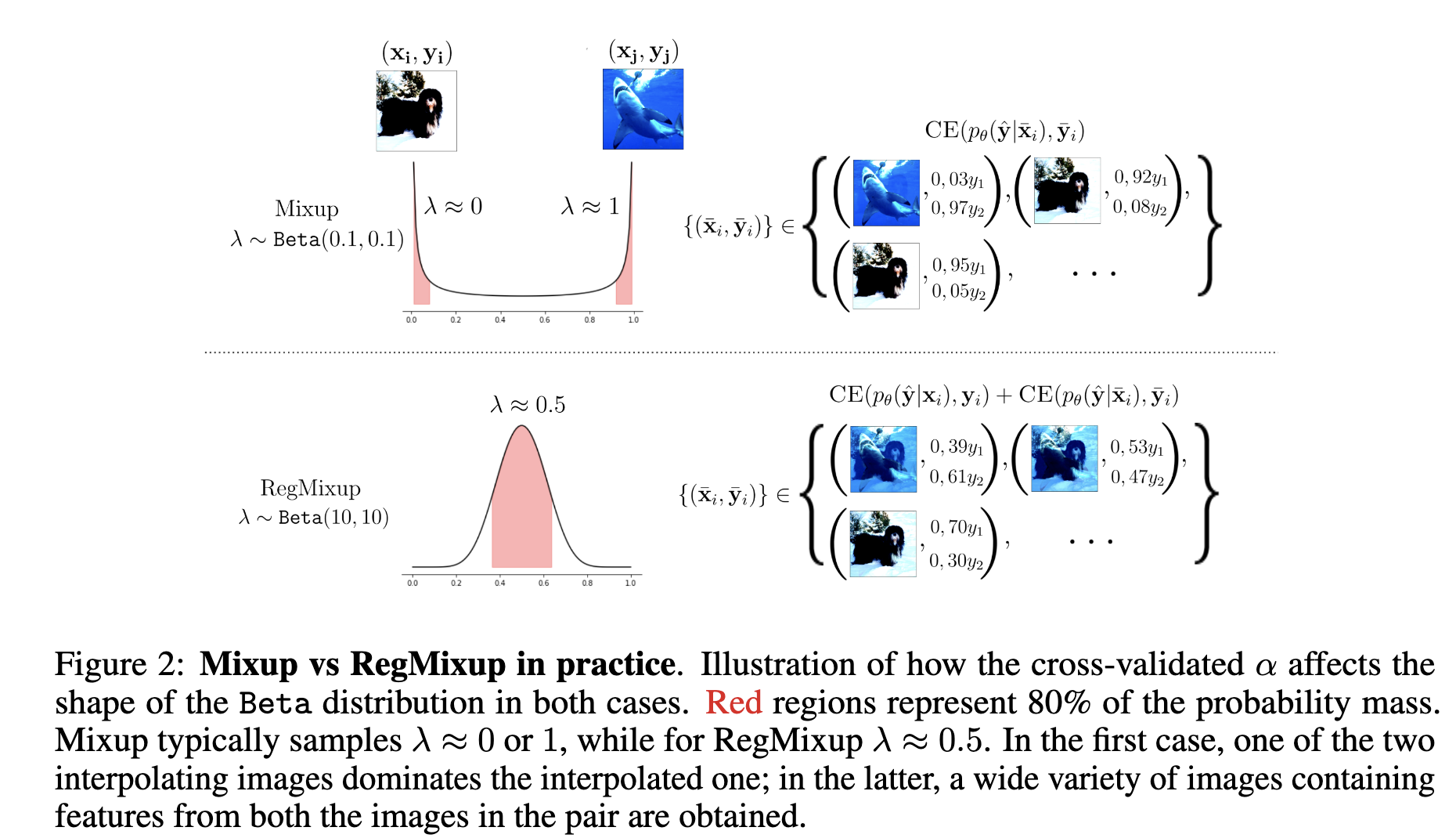
RegMixup
Using Self-Supervised Learning Can Improve Model Robustness and Uncertainty
以 rotation prediction 作为 pre-text task 进行 self-supervised training,能够很好地提升模型 robustness:
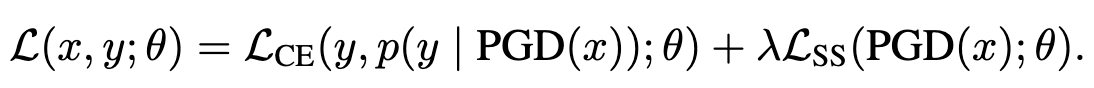
Unsupervised Adversarial Training (UAT)
对抗 adversarial attack 的一个有效方法是增加更多的训练数据,但收集 labeled dataset 毕竟成本比较高。作者提出了一个基于 unsupervised learning 的方法来从海量无标签数据中进行学习,从而增强模型的 robustness。无监督 smooth loss 可以是以下两种形态:
- Unsupervised Adversarial Training with Online Targets (UAT-OT)
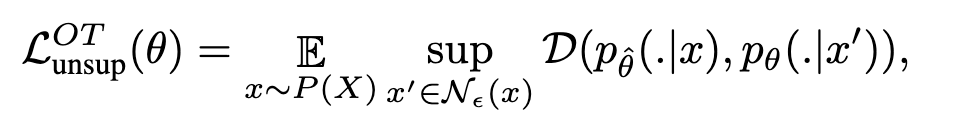
- Unsupervised Adversarial Training with Fixed Targets (UAT-FT)
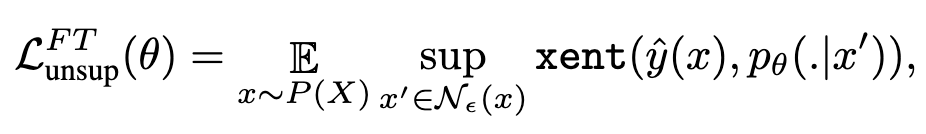
Adversarial Robustness is at Odds with Lazy Training
Lazy training 方式训练的 DL 模型容易受到 adversarial attack。
Lazy training:网络在训练过程中的权重变化较小,使得网络在初始化附近表现得像它的线性化。在懒惰训练下,神经网络容易受到对抗性攻击,因为网络在初始化附近的局部线性特性使得对抗性攻击更容易找到梯度上升路径,从而产生错误预测。
提高网络鲁棒性以应对对抗性攻击的方法:
- 在训练过程中使用对抗训练:通过生成对抗性样本并将其与原始样本一起训练网络,可以提高网络的鲁棒性。
- 使用更大的网络宽度:增加网络宽度可以提高网络的鲁棒性,但需要注意网络宽度与输入维度之间的平衡。
- 探索更强的防御方法:研究新的防御方法可能有助于找到更有效的方法来抵御对抗性攻击。
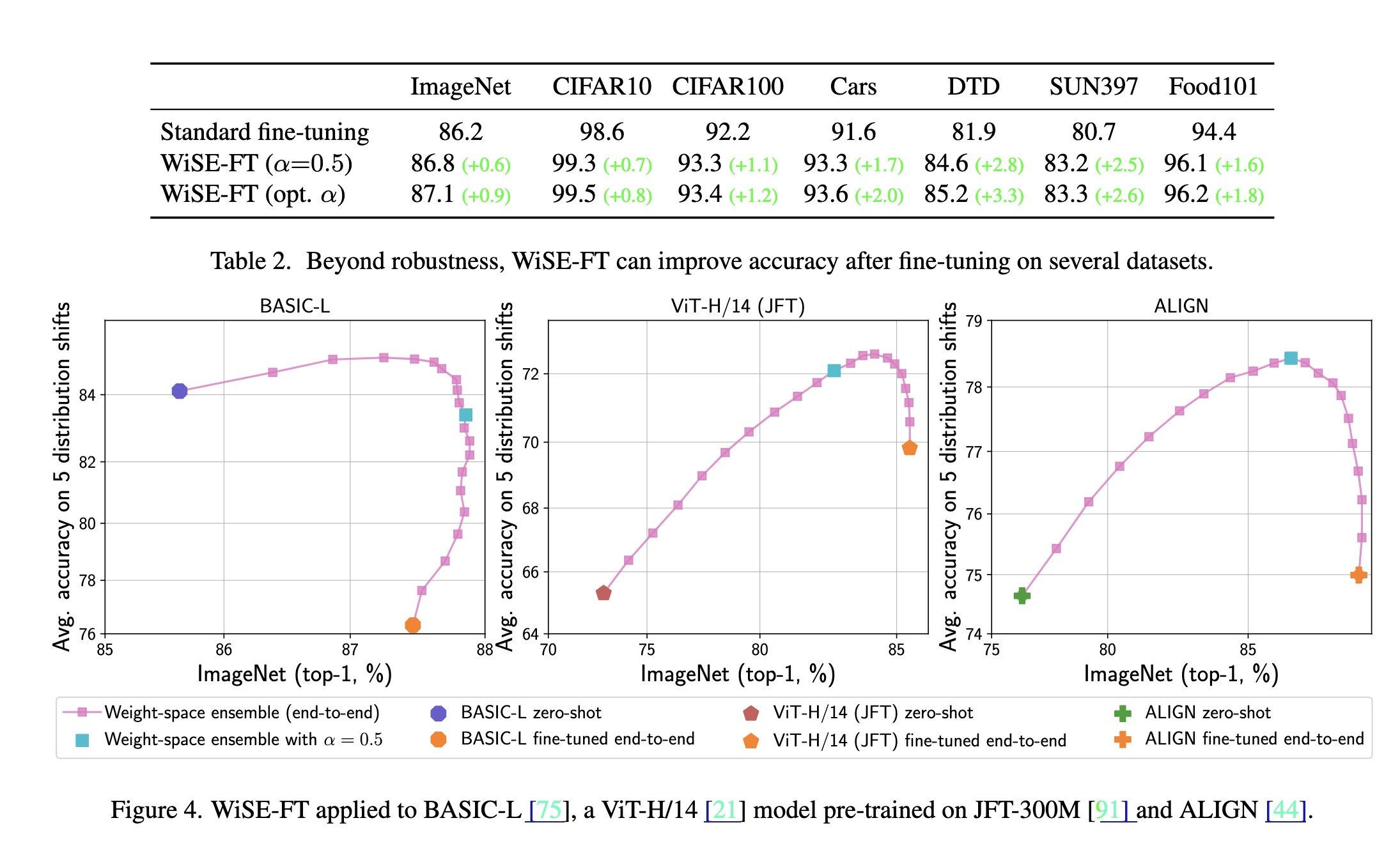
Robust fine-tuning of zero-shot models
主要分为两个步骤:
- 首先正常 fine-tuning
- 在 weight space 进行 interpolation 操作(和 SWA 其实没啥本质区别…)
这种方法充分利用了零样本模型在分布偏移下的鲁棒性,同时保留了微调模型在目标分布上的高性能。
Reference
- Zhang, Chiyuan, Samy Bengio, and Yoram Singer. “Are all layers created equal?.” The Journal of Machine Learning Research 23.1 (2022): 2930-2957.
- Liu, Mengchen, et al. “Analyzing the noise robustness of deep neural networks.” 2018 IEEE Conference on Visual Analytics Science and Technology (VAST). IEEE, 2018.
- https://neptune.ai/blog/adversarial-attacks-on-neural-networks-exploring-the-fast-gradient-sign-method
- 【炼丹技巧】功守道:NLP中的对抗训练 + PyTorch实现
- Izmailov, Pavel, et al. “Averaging weights leads to wider optima and better generalization.” arXiv preprint arXiv:1803.05407 (2018).
- Zhang, Haoyang, et al. “Swa object detection.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2012.12645 (2020).
- Wortsman, Mitchell, et al. “Model soups: averaging weights of multiple fine-tuned models improves accuracy without increasing inference time.” International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR, 2022.
- Yang G, Zhang T, Kirichenko P, et al. SWALP: Stochastic weight averaging in low precision training[C]//International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR, 2019: 7015-7024.
- Pinto, Francesco, et al. “Regmixup: Mixup as a regularizer can surprisingly improve accuracy and out distribution robustness.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.14502 (2022).
- Pinto, Francesco, et al. “Using mixup as a regularizer can surprisingly improve accuracy & out-of-distribution robustness.” Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 35 (2022): 14608-14622.
- Hendrycks, Dan, et al. “Using self-supervised learning can improve model robustness and uncertainty.” Advances in neural information processing systems 32 (2019).
- Alayrac, Jean-Baptiste, et al. “Are labels required for improving adversarial robustness?.” Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 32 (2019).
- Wang, Yunjuan, et al. “Adversarial robustness is at odds with lazy training.” Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 35 (2022): 6505-6516.
- Wortsman, Mitchell, et al. “Robust fine-tuning of zero-shot models.” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2022.
